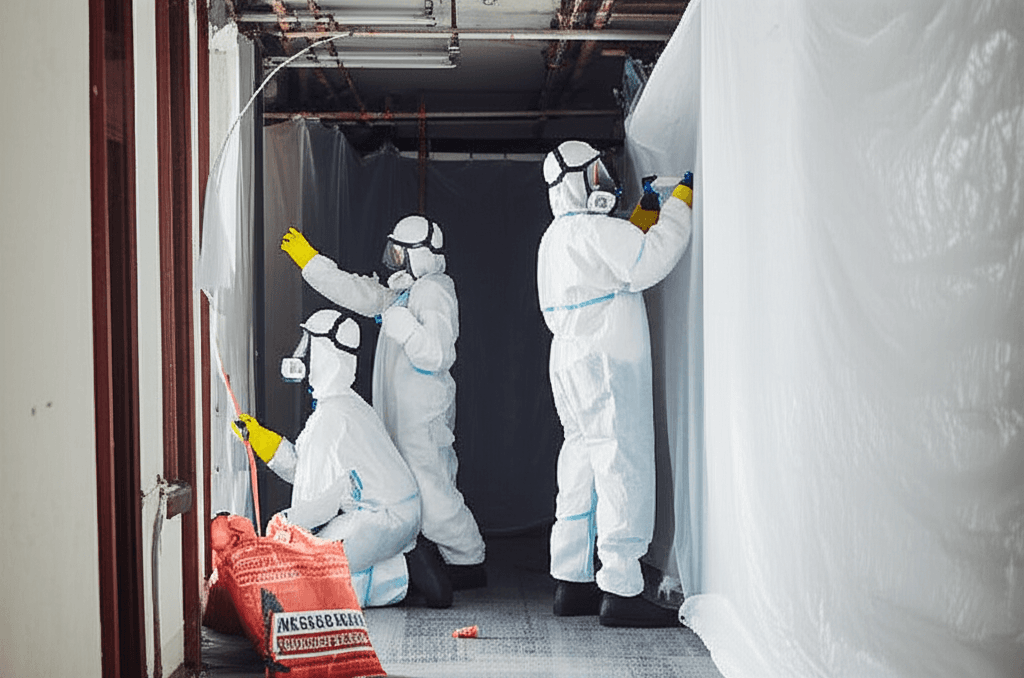
Lead-based paint is still present in many Calgary schools, churches, and pre-1980 homes. When renovation or demolition work disturbs those coatings, lead dust can contaminate air and surfaces, putting occupants and workers at risk. Alberta's regulatory framework outlines clear expectations for testing, containment, and waste disposal to keep projects safe.
This article explains the rules that govern lead paint abatement across Alberta, including how they intersect with municipal permits and occupational health legislation.
Whether you're planning a minor repaint or a major restoration, understanding these requirements—and how they connect with resources like the Calgary asbestos abatement hub—keeps your team compliant and your budget on track.
Regulatory Overview
Lead paint work in Alberta falls under several acts: the Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) Code, the Environmental Protection and Enhancement Act, and in some cases the Public Health Act. Employers must assess hazards, implement controls, and ensure worker training. Municipalities, including Calgary, may add permit conditions requiring proof of lead-safe practices before issuing approvals.
For federally owned buildings or projects funded by federal agencies, the Canadian Environmental Protection Act may also apply. Understanding which regulations intersect with your project is the first step toward compliance.
Conducting Lead Risk Assessments
Before work begins, hire a qualified consultant to conduct a lead risk assessment. They collect paint chip or dust wipe samples and may use X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analyzers to map lead concentrations. Results determine whether the work is low-, moderate-, or high-risk, influencing containment strategies and personal protective equipment requirements.
In multi-hazard environments, combine lead assessments with Calgary asbestos testing to streamline planning. Coordinated sampling reveals whether asbestos, mould, or silica hazards also need attention, allowing you to schedule specialized crews efficiently.
Worker Training and Competency
Alberta OHS mandates that employers provide training on lead hazards, safe work procedures, hygiene practices, and emergency response. Workers must understand how to set up containments, use HEPA vacuums, and handle waste without spreading contamination. Supervisors should be familiar with both provincial regulations and any project-specific protocols set by consultants.
Document all training sessions, including attendance records and curriculum outlines. Inspectors often request this proof during site visits, and it demonstrates your commitment to health and safety.
Engineering Controls and Work Practices
Containments must prevent dust migration. Install poly sheeting, negative air machines, and sticky mats at entry points. Wet methods, such as misting surfaces before scraping, reduce airborne particles. Mechanical ventilation should exhaust outdoors through HEPA filtration. Workers must wear appropriate respiratory protection, often half-face or full-face respirators, depending on exposure levels.
For projects in occupied buildings, schedule work during off-hours and coordinate with building management to notify tenants. When lead paint is present alongside asbestos, partner with a certified asbestos abatement contractor Calgary trusts to sequence tasks without cross-contamination.
Air Monitoring and Clearance
Air monitoring verifies that controls are effective. Industrial hygienists collect personal and area samples to measure lead concentrations during work. If levels approach occupational exposure limits, additional engineering controls or respiratory protection may be required.
Post-abatement clearance involves visual inspections and dust wipe sampling. Passing results confirm that surfaces are safe for re-occupancy. Keep copies of all laboratory analyses; they provide defensible proof of compliance should questions arise later.
Waste Handling and Disposal
Lead-contaminated waste must be stored in sealed, labelled containers and transported to approved facilities. Follow Transportation of Dangerous Goods (TDG) requirements when hauling large volumes. Maintain manifests that track waste from the site to the disposal location.
Where projects also generate asbestos waste, keep materials segregated to meet disposal regulations. Coordinate pickups so haulers can manage both streams efficiently without compromising safety protocols.
Record-Keeping and Reporting
Comprehensive documentation supports compliance and risk management. Maintain files containing risk assessments, worker training records, air monitoring results, waste manifests, and clearance reports. Store digital copies in secure repositories that stakeholders can access when needed.
Some projects, particularly those in schools or healthcare facilities, require public reporting or communication with occupants. Prepare summaries that explain the work, safety measures, and clearance outcomes to build trust and transparency.
Integrating Lead Abatement With Other Renovation Activities
Lead abatement rarely happens in isolation. Coordinate with painters, carpenters, and mechanical contractors to prevent recontamination. Ensure that new finishes are compatible with encapsulants or primers used to stabilize remaining lead-based coatings.
If mould is present due to chronic moisture, engage mould remediation in Calgary professionals to clean and dry surfaces before repainting. Integrated planning keeps schedules tight and ensures all hazards are addressed comprehensively.
Staying Ahead of Regulatory Changes
Regulations evolve as research reveals new health impacts. Stay connected with industry associations and subscribe to Alberta OHS bulletins to track updates on exposure limits or reporting requirements. Conduct annual reviews of your lead safety program to ensure policies reflect current standards.
When in doubt, consult with environmental lawyers or regulatory specialists. Proactive advice is far cheaper than reacting to fines or stop-work orders after an inspection.
Communicating With Stakeholders
Lead projects can cause anxiety for occupants and neighbours. Prepare clear notifications that outline the scope, schedules, and safety measures in plain language. Provide contact information for project leads so questions are addressed promptly.
After completion, share summary reports that highlight clearance results and future maintenance recommendations. Linking to municipal resources and the Calgary asbestos abatement hub helps stakeholders understand how the work fits into broader hazard management strategies.
When projects overlap with other hazards, coordinate messaging with your Calgary asbestos removal and mould remediation in Calgary partners. Presenting a unified plan reassures audiences that every risk is being handled by qualified professionals.
Conclusion
Navigating lead paint regulations in Alberta requires diligence, but the payoff is healthier buildings and lower liability. By combining professional assessments, rigorous controls, and thorough documentation, property owners and contractors can deliver projects safely and confidently.
Keep compliance front-of-mind, and lead abatement becomes a manageable component of your renovation strategy rather than a roadblock.
Plan your Calgary lead paint removal safely
Request a Calgary renovation estimate or call 403-617-0255 to coordinate with Makki Abatement's certified team.